Further information on CNGP reporting
This page contains further information on reporting requirements for agencies.
This page contains further information on reporting requirements for agencies.
2024 reporting covers emissions from the financial year 2023/24 and calendar year 2023. For earlier reporting, go to the Reporting dashboard.
Participating organisations are required to report:
Organisations report this information to the programme lead by 1 December each year.
Agencies are required to obtain independent third-party assurance that their emissions inventory has been prepared in accordance with ISO 14064-1 and/or the GHG Protocol for their base year and current year of reporting. Acceptable assurance levels include reasonable and limited assurance.
Organisations select their own base year, no earlier than 2015/16 and no later than 2023/24. The ‘Base Year’ referred to at the programme level represents the cumulative total of emissions from each agency's base year.
CNGP organisations are required to set gross emissions reduction targets for 2025 and 2030 according to the reduction potential within their agency, and with reference to an emissions pathway consistent with limiting global warming to 1.5-degrees.
A recommended framework was developed based on a simplified version of the Science Based Targets initiative, as described below:
Following this methodology, combining base years, a cumulative 1.5-degree aligned target for 2025 would be 17.6% for Tranches 1 and 2, and 18% for Tranche 3.
Further information on CNGP target-setting
The GHG Protocol places emission sources into scope 1, scope 2 and scope 3 activities.
The emissions reported from CNGP organisations cover Scope 1, 2 and mandatory Scope 3 emissions. Some organisations have chosen to expand their reporting to include further non-mandatory Scope 3 sources, such as commuting or supply chain emissions, under their official target as they may have significant reduction potential. The diagram below shows the mandatory emission sources from Scope 1-3, and some examples of non-mandatory sources which can be incorporated.
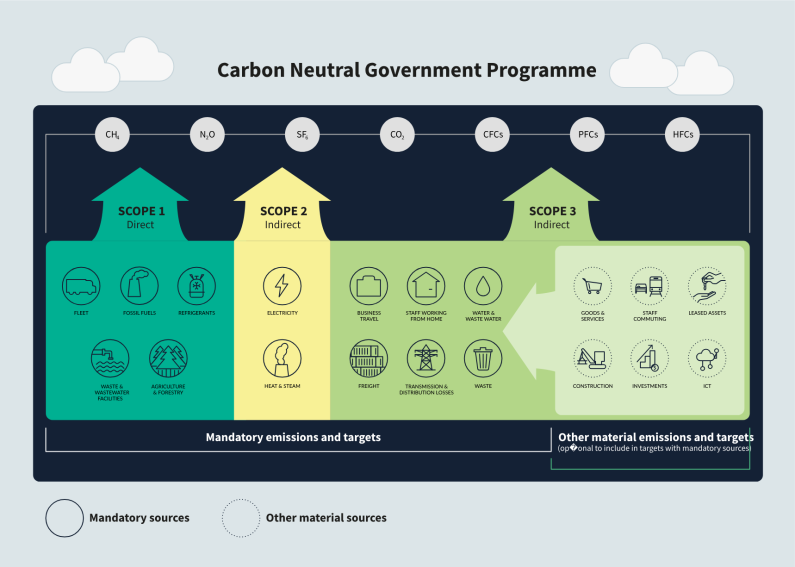
| Scope 1:Direct | Scope 2: Indirect | Scope 3: Indirect- mandatory | Scope 3: Indirect: Optional to include in targets |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
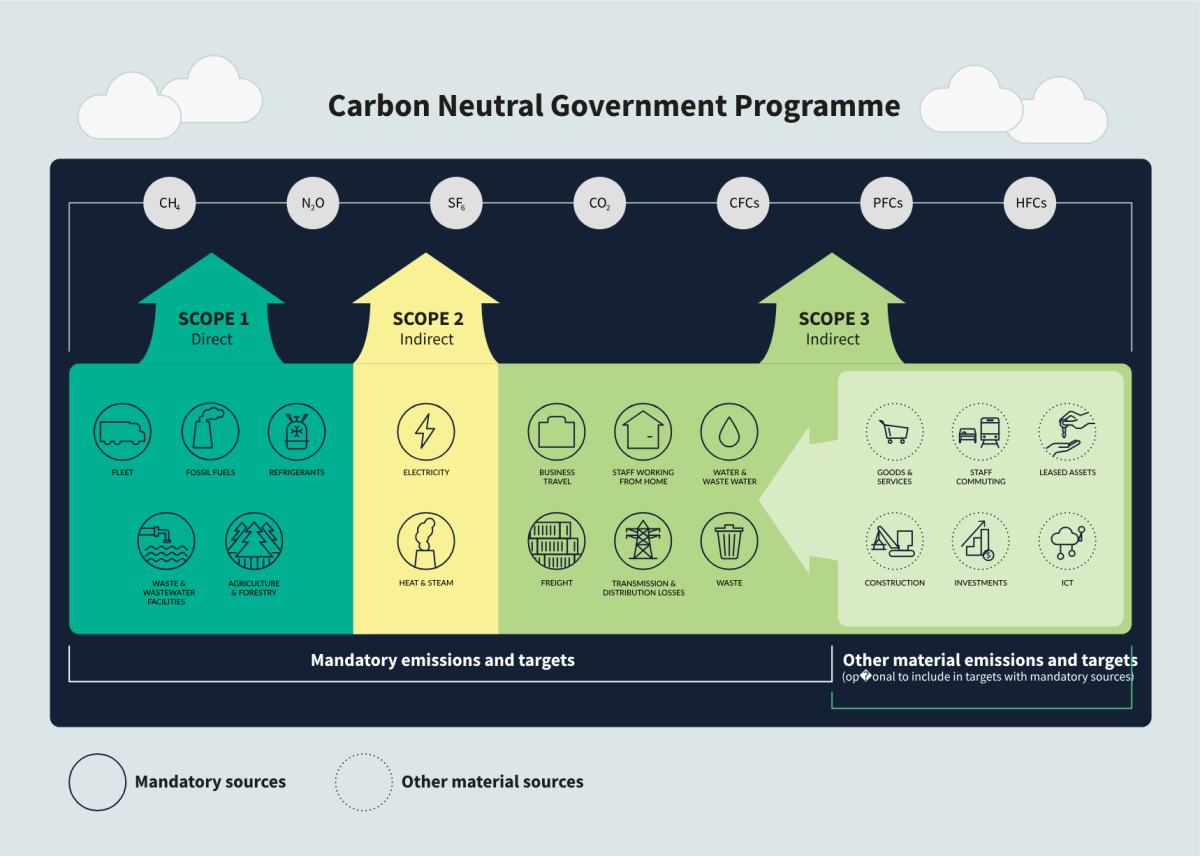
| Scope 1:Direct | Scope 2: Indirect | Scope 3: Indirect- mandatory | Scope 3: Indirect: Optional to include in targets |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|